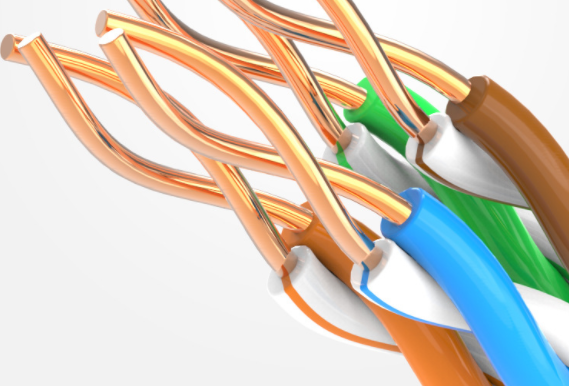
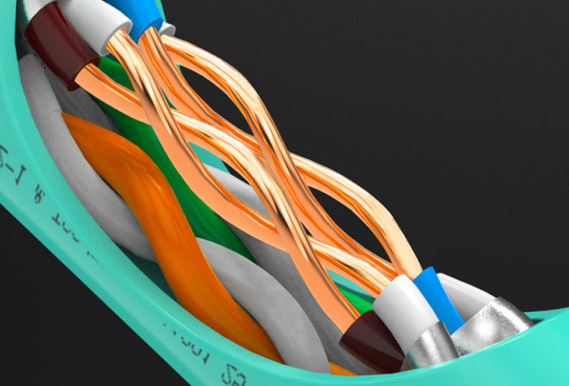
There are several ways to connect network cables
Two ways I. Production of parallel lines Second, the production of crossover cable 1. Parallel line production End A: White Orange / Orange / White Green / Blue / White Blue / Green / White Brown / Brown B: White Orange / Orange / White Green / Blue / White Blue / Green / White Brown / Brown 2. Making crossover cable In the online sequence, the 1-3, 2-6 exchange method was used. One end was made with 568B, and the other was made with 568A. A end: white green / green / white orange / blue / white blue / orange / white brown / brown Terminal B: White Orange / Orange / White Green / Blue / White Blue / Green / White Brown / Brown
2023-02-16
Does the length of the network cable affect the speed of the network?
The network cable cannot exceed 100 meters, and it will cause network failure. So why can't the network cable exceed 100 meters? It should be the standard that limits the length of the network cable. There are clear regulations in the engineering design of the integrated wiring system. The maximum length of the channel of the wiring subsystem cannot exceed one hundred meters. For example, in the 100Mb / s Ethernet physical layer, the maximum length of 100BASE-TX and 100BASE-T4 network segments is one hundred meters. Now that the standard limits the length of the network cable, have you ever wondered why the network standard specifies the length of the network segment in this way? In fact, we have to find the answer from our lives. To give a very simple example of life, you can hear each other very clearly when you talk to others face to face. As the distance increases, it becomes more and more difficult to hear each other. This example illustrates the reason that sound is lost during transmission. As the distance between two people is farther away, the greater the loss of sound transmission, the weaker the sound of being able to hear each other. Returning to the network cable from the above example, the network cable is also a wire. Since the wire has resistance, there is power loss when there is resistance. Therefore, the longer the network cable, the greater the signal attenuation. The receiver wants to receive the signal correctly. The length of the network cable cannot exceed one hundred meters. Since the standard stipulates that the length of the network cable cannot exceed one hundred meters, it is also implemented in this standard when designing and producing. Therefore, the length of the network cable can certainly guarantee the normal transmission of data within 100 meters, and the transmission effect beyond 100 meters cannot be guaranteed. In summary, the length of the network cable cannot exceed one hundred meters, but the main reason depends on the electrical characteristics of the network cable.
2023-02-16
Do you know the six materials of the network cable?
The commonly used network cables are generally super five or six types of cables. Although they are all network cables, there are also several types of network cables. Let's take a look at the six materials of network cables today. Four iron four aluminum network cable Four iron and four aluminum is the worst quality network cable among them, the transmission quality is poor, and it is easy to appear attenuation. A 100-meter resistor is about 50 ohms and can transmit up to 60 meters. The differences are as follows: A. For the aluminum mesh cable, the inner layer has no luster and will break when pulled; B. The simplest method is this. Use a magnet to attract the network cable. If it is attracted, it proves that the network cable contains iron; C. The four cores of iron and aluminum are of different materials, which are much harder than all copper and copper-clad aluminum materials; D. Burned with fire, the hardness of iron is very high. Burned with fire will not soften quickly. 2. Copper clad aluminum network cable The material of the copper-clad network cable is covered with a layer of oxygen-free copper on the copper core marked with aluminum or aluminum / steel alloy core. Because aluminum is less conductive than copper, the DC resistance of copper-clad aluminum conductors is greater than that of pure copper conductors. If used for power, copper-clad aluminum conductors will cause additional power consumption and lower voltages. The resistance of 100 meters is about 28 ohms. If you compile it and buy it, it can transmit about 100 meters, with poor oxidation resistance and short service life. The tensile strength of copper-clad aluminum is not as great as that of copper conductors, that is, the tensile strength is low. Do not pull the cable body vigorously during use. 3. Oxygen-free copper network cable We can see from the copper core of the wire, in general, all copper network cable is the new material of the outer layer, and oxygen-free copper is the new material of the inside and outside. You can check the gloss of the thread and cut it to see if it can be thinned. The newer gloss is the new material, and the thinner is the new material. However, the current all-copper network cable also tends to be new inside and outside, so it can only be used as a basic basis. If you use a knife to scrape the surface or cross section: Oxygen-free copper network cable: scrape off the surface layer, the color is basically the same, and the cross-section color is uniform, no difference; Bronze wire: Scratching indicates a layer, the surface and internal colors are different, and the cross section is a little white. If you burn it with fire, the surface of the whole copper is coated with a layer of oxygen-free copper. During the burning process, you will find that the outer layer of oxygen-free copper will melt, and then wipe it with paper. It will be difficult to change the copper core back to the original yellow. copper; Oxygen-free copper contains no impurities. During the burning process, only the surface is oxidized. After wiping with paper, it will still return to its original yellow color. According to the standards, the oxygen content in oxygen-free copper network cables is not more than 0.003%, the total content of magazines is not more than 0.05%, and the purity is greater than 99.95%. Therefore, oxygen-free copper has high conductivity, processability and welding performance, corrosion resistance and low temperature. Good performance, suitable for high quality network cable material. The resistance of oxygen-free copper network cable is less than 10 ohms within 100 meters, and can transmit about 120-150 meters. The signal transmission distance is long and the packet loss rate is low. Copper, network stability is guaranteed, strong oxidation resistance, long life. 4. High-conductivity copper network cable The high-conductivity copper network cable does not only contain copper-silver components, but is actually a copper-aluminum-silver alloy high-performance network cable. It is also commonly referred to as copper-clad silver. It has the characteristics of low resistance and long transmission distance. Compared with all copper and iron-aluminum network cables, the resistance is about 20 ohms for 100 meters and can transmit 120 meters, but the oxidation resistance is poor and the life is not long. 5. Copper-clad copper network cable The copper-clad copper network cable refers to a layer of oxygen-free copper plated on the outside of the bronze, so it is also called a bronze network cable. This kind of network cable is generally ignored by everyone, and not many people understand it. The conductor of the bronze network cable belongs to secondary furnace copper and contains more impurities. The resistance of 100 meters is about 40Ω, and it can transmit about 80 meters. It has strong oxidation resistance and long service life. The resistance of bronze is much higher than that of ordinary c
2023-02-16
Why the bigger the return loss, the better
Return loss refers to the decibel ratio of the ratio of backward reflected light (scattered light continuously transmitted to the input end) to the input light at the fiber connection. The larger the return loss, the better, in order to reduce the reflected light on the light source and the system. Impact. The return loss is -10 lg [(reflected power) / (incident power)]. Now that the three networks are integrated, the optical fiber is used to enter the home, and the interfaces connected to the television signal must use APC connectors, which is a kind of beveled optical fiber connectors. The return loss of this connector can reach 55dB. The return loss can be understood as the matching degree of the line, that is, the position of the light source, the input end, and the input of the line. The measurement can be said to be the starting end of the test. The backward reflected light is equivalent to being reflected back at the end. Light, you want to have a glass at the end. You can see what is behind the glass with a flashlight. When a piece of light passes through, there is always a part of the glass that is reflected back. If the more is returned, the glass is brighter and you cannot see it. Things, so you have to reflect less glass and not reflect (impossible). You can better see the back. The return loss is actually a negative value. -10 lg [(reflected power) / (incident power) this is Proportion formula. It can be seen from the formula that the incidence is total. Calculate the ratio of reflection to the total. The smaller the ratio is, the larger the value is (10% is smaller than 1%).
2023-02-16
In order to let everyone have a comprehensive understanding of twisted pair, we first introduce the common types and characteristics of twisted pair. Twisted pair in computer LAN can be divided into two categories: unshielded twisted pair (UTP) and shielded twisted pair (STP): STP is covered with a layer of metal material to reduce radiation and prevent information from being intercepted. It has a higher data transmission rate, but the price is higher and the installation is more complicated; UTP has no metal shielding material and is only covered with a layer of insulating rubber. The price is relatively cheap and the networking is flexible. Except for some special occasions (such as severe electromagnetic radiation, high requirements for transmission quality, etc.) in the wiring using STP, we generally use UTP. The UTPs currently used can be divided into 3 types, 4 types, 5 types, super 5 types, 6 types, and 6 types. Among them: Category 3 UTP meets the requirements of Ethernet (10Mbps) for transmission media and is an important transmission medium in early networks; Category 4 UTP is later than Category 3 due to the introduction of the standard, and transmission performance is not comparable to Category 3 UTP. How much it is increased, so it is generally less used; Category 5 UTP is the preferred medium for Fast Ethernet (100Mbps) because of its low price and high quality; Gigabit Ethernet (1000Mbps) is used for Category 5 UTP. Super 5 has less attenuation, less crosstalk, higher ACR and Structural Return Loss, smaller delay error, and greatly improved performance. The maximum transmission rate for Category 5 lines is 250Mbps. 哪些 What are the super five types of network cables? Super Category 5 unshielded twisted pair is also called UTP, four pairs of twisted pairs. Super Category 5 cables are mainly divided into 04,045,05 diameters. Category 5 network cables are mainly used in 100M networks and transmit 100M. Signal! Unshielded twisted pair cable is the most common network cable. It is widely used. Not only does network wiring need to be used, many instruments now use four twisted pair cables because they can be bought everywhere. It is most convenient to use him for data transmission or transfer data. Super five types of unshielded twisted-pair wires are not only separated from the core, but also divided from a variety of materials. Most of the commercially used four-iron-four-aluminum network cables, and also all copper network cables, or copper-clad silver network cables! Is to find the right network cable according to our own needs. "Ultra-Five" refers to UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair). Unshielded twisted pair cable consists of multiple pairs of twisted pairs and a plastic sheath. Five categories refer to the five different quality levels defined by the International Electrical Industry Association for twisted-pair cables. Category 5 unshielded twisted pair cable is a cable that appears after improving some of the performance of the existing category 5 shielded twisted pair. Many performance parameters, such as near-end crosstalk, attenuation crosstalk ratio, and return loss, are all different. Increase, but its transmission bandwidth is still 100MHz. Super Category 5 twisted pair also uses 4 twisted pairs and 1 tensile wire. The color of the pair is exactly the same as Category 5 twisted pair, which are white orange, orange, white green, green, white blue, blue, white Brown and brown. The bare copper wire diameter is 0.51mm (wire gauge is 24AWG), the insulation wire diameter is 0.92mm, and the UTP cable diameter is 5mm. Although Category 5 unshielded twisted-pair cables can also provide transmission bandwidths of up to 1000Mb / s, they often need the help of expensive special equipment. Therefore, it is usually only applied to 100Mb / s Fast Ethernet to achieve the connection from desktop switches to computers. If you don't plan to upgrade your network to Gigabit Ethernet in the future, you may wish to use Category 5 unshielded twisted-pair wires in horizontal cabling.
2023-02-16
What's the difference between Category 5, Category 5, and Category 6 cables?
The twisted-pair wires used in our comprehensive wiring (daily use is called network cables) are classified into three types, four types, five types, super five types, six types, ultra six types, seven types, etc. according to the classification of electrical performance. Types of. Category 3 and Category 4 twisted pair cables have been eliminated in the market. Category 5 is an infrequently used type. Common types of network cables are Super Category 5 and Category 6 network cables. Category 7 network cables are expensive and not widely used. In principle, the larger the number of Category 5, Category 5, Category 6, and Category 6 network cables, the newer the version, the higher the bandwidth, and the price will increase accordingly. Category 5 network cables will be marked with "CAT5" on the outside, with a transmission bandwidth of 100MHz, which is used for voice transmission and data transmission at a maximum transmission rate of 100Mbps. It is mainly used for 100M networks and 10M networks, and has been replaced by Category 5 cables. Cat.5e cable with “CAT5e” on the outer cover, transmission bandwidth can be as high as 1000Mb / s, but it is generally only used in 100Mb / s networks, and only connects desktop switches to computers. Support for expensive special equipment. In the transmission of 100M networks, the ultra-category 5 unshielded network cable has less attenuation and stronger anti-interference ability than the ordinary category 5 network cable when transmitting signals. In a 100M network, the interference level of user equipment is only 1/4 of that of ordinary Category 5 lines. The outer sheath of Category 6 network cables is marked with "CAT6", which generally refers to unshielded network cables. It is mainly used in Gigabit networks, and its transmission performance is much higher than that of Category 5 network cable standards. Super Cat 6 network cable is labeled "CAT6e". Cat 6 Cat 6e cable is also called 6A, which can support 10 Gigabit Internet access. At present, it can reach a maximum of 500MHZ, which is twice as much as Cat 6 cable. 1. Differences between Category 6 and Category 5 network cables 1) The internal structure of Category 6 and Category 5 network cables is different. The internal structure of Category 6 network cables has a cross skeleton, and the four pairs of twisted pair cables are placed in the cross skeleton. Within the four grooves, it solves the common crosstalk problem in six types of transmission. 2) The size of copper cores of Category 6 and Category 5 cables is different. Category 5 cables have a copper core below 0.45mm, Category 5 cables are 0.45-0.51mm, and Category 6 cables are standard 0.56-0.58mm. 2. The differences between Category 6 and Category 6 cables: Category 6 uses gear-shaped cable troughs to effectively change the enhanced signal and prevent signal attenuation to a minimum. Note that the cross skeleton is not the only standard for Category 6 network cables. Some Category 6 network cables are isolated by one word, and some do not even have them. As long as they can meet the standards, they can pass the test. But most manufacturers ca n’t produce six types that meet the standards without ten
2023-02-16
What is the difference between fiber and cable?
Optical fiber is a thin and flexible medium that transmits light beams. An optical fiber cable consists of a bundle of fibers, referred to as an optical cable. The optical fiber is the core part of the optical cable, and the optical fiber constitutes the optical cable through the protection of some components and the protective layer. Optical fiber is usually made of quartz glass, and its double cross-section is a concentric cylinder with a small cross-sectional area.
2023-02-16
There are several ways to connect network cables
Two ways I. Production of parallel lines Second, the production of crossover cable 1. Parallel line production End A: White Orange / Orange / White Green / Blue / White Blue / Green / White Brown / Brown B: White Orange / Orange / White Green / Blue / White Blue / Green / White Brown / Brown 2. Making crossover cable In the online sequence, the 1-3, 2-6 exchange method was used. One end was made with 568B, and the other was made with 568A. A end: white green / green / white orange / blue / white blue / orange / white brown / brown Terminal B: White Orange / Orange / White Green / Blue / White Blue / Green / White Brown / Brown
2023-02-16
Does the length of the network cable affect the speed of the network?
The network cable cannot exceed 100 meters, and it will cause network failure. So why can't the network cable exceed 100 meters? It should be the standard that limits the length of the network cable. There are clear regulations in the engineering design of the integrated wiring system. The maximum length of the channel of the wiring subsystem cannot exceed one hundred meters. For example, in the 100Mb / s Ethernet physical layer, the maximum length of 100BASE-TX and 100BASE-T4 network segments is one hundred meters. Now that the standard limits the length of the network cable, have you ever wondered why the network standard specifies the length of the network segment in this way? In fact, we have to find the answer from our lives. To give a very simple example of life, you can hear each other very clearly when you talk to others face to face. As the distance increases, it becomes more and more difficult to hear each other. This example illustrates the reason that sound is lost during transmission. As the distance between two people is farther away, the greater the loss of sound transmission, the weaker the sound of being able to hear each other. Returning to the network cable from the above example, the network cable is also a wire. Since the wire has resistance, there is power loss when there is resistance. Therefore, the longer the network cable, the greater the signal attenuation. The receiver wants to receive the signal correctly. The length of the network cable cannot exceed one hundred meters. Since the standard stipulates that the length of the network cable cannot exceed one hundred meters, it is also implemented in this standard when designing and producing. Therefore, the length of the network cable can certainly guarantee the normal transmission of data within 100 meters, and the transmission effect beyond 100 meters cannot be guaranteed. In summary, the length of the network cable cannot exceed one hundred meters, but the main reason depends on the electrical characteristics of the network cable.
2023-02-16